Creating Emotional IR Images From Your Heart

Using the Fuji X Pro 1 for Infrared
Infrared photography means so many things to me… It is more than a type of photography, rather a passion or better yet an addiction! I have a LOT of experience in Infrared, I have a book in work on it, but MOST IMPORTANTLY, I have practiced the art of creating emotionally charged Infrared images for longer than I can remember, even as long as 45 years ago with film. Here, today, I will disscuss with you the technical details of using your Fuji X Pro 1 camera system to create these emotionally powerful images as well.

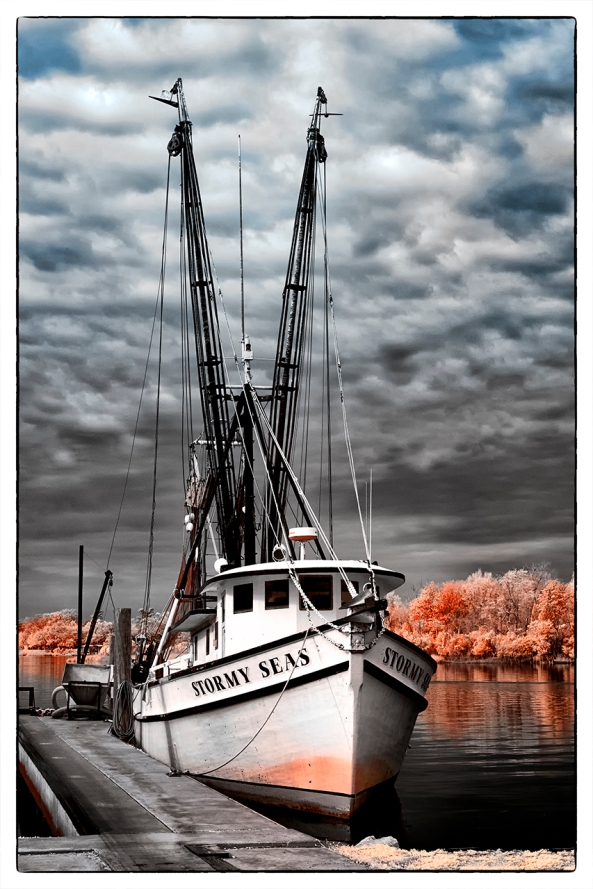
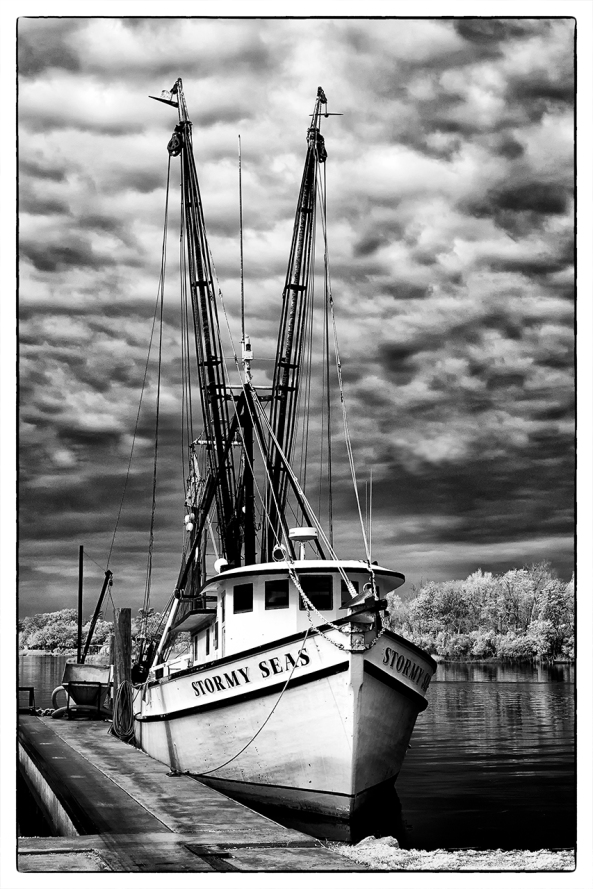
X Pro 1 Faux Color IR Image with only the channel swap
Understand this, you can create Infrared images several different ways:
- Film: Rolli makes a great 720nm IR film in many different formats that with the addition of a 720nm filter on your lens will create great IR images at 100 ISO, and with no filter great B&W images at 400 ISO!
-

Hoya R72
Standard Digital COLOR Camera: With the addition of a 720nm or 850nm IR filter on your camera lens your camera can capture Infrared images. There is a tradeoff to this way though because each camera manufacturer places some sort of UV/IR blocking filter over the image sensor that allows only visible light to pass through. Some of these filters are weaker than others and these cameras make for a system that will do well in Color and OK in Infrared with reasonable IR exposure times around a second or two. Others have a strong filter allowing only a small amount of IR energy to pass. These require VERY LONG exposure time in order to overcome this filter. The Fuji X Pro 1 is one of the cameras with a weaker filter! This is exciting because it enables you to easily create IR images with an unmodified camera system!
- Converted Infrared Camera: This type of system is the most popular by far. There are 2 types:
- Full Spectrum conversion: The internal UV/IR blocking filter is removed and replaced with a clear glass filter. You can then program the camera with an external IR filter in any range from UV to Color to Infrared! This is the most adaptable IR system but costly because IR filters for your different lens sizes are expensive!
- Dedicated Infrared Conversion: This type has the internal UV/IR blocking filter removed and replaced with a specific IR pass filter and will create IR images in that band only.
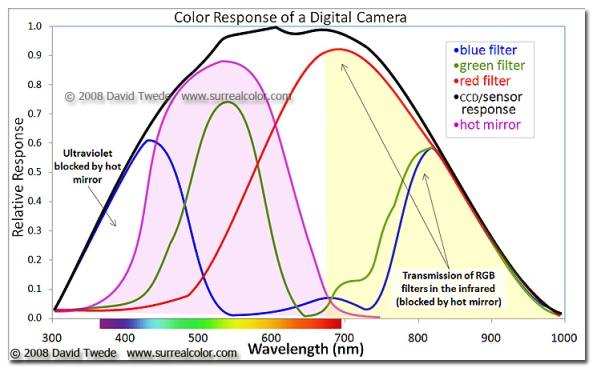
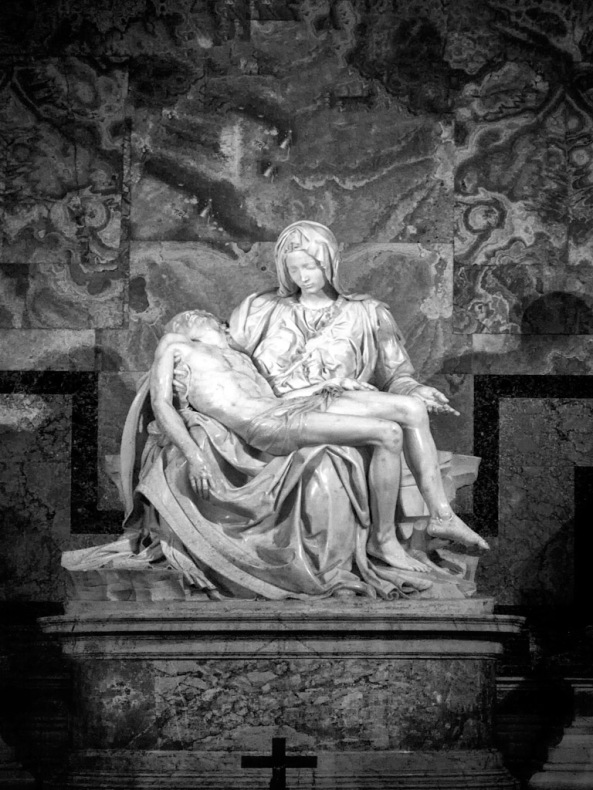
What your camera sees!
So with regard for the Fuji X Pro 1 system we are going to discuss option #2, the standard color camera with an external IR filter attached to its lens. But you ask: “What filter can I use?”. Well since we are not modifying the internal UV/IR blocking filter you must understand that the camera will pass normal visible colors as well as IR if the external filter allows it. This is both good and bad! If you were to install a 590nm IR filter on your lens the camera, it would see everything from 590nm up to 1000nm. But because the internal UV/IR blocking filter allows much more visible light than IR through, it will poison the exposure metering system. It is going to see the vast majority of the light as color (red) and expose for that rather than the IR portion. So attempting to do this will cause very unreliable exposure and great frustration on the part of the photographer.
What we need is to attach an IR filter that blocks ALL of the visible light and only passes IR to the sensor! So it is best to choose a 720nm IR pass filter to your lens like the Hoya R72 or a 800nm B&W IR only filter like the B+W 093. The higher you go in nm the longer the exposure time will be…
Now, knowing that we are going to use the 720nm filter which will only pass IR energy from 720nm and up while blocking ALL of the visible light our metering system will now function as it should!
Considerations of problems that must be overcome within the X Pro 1 to get good IR images
- Even though the Fuji X Pro 1 has a weak UV/IR blocking filter there is still one there. Exposure time at a normal low noise ISO of 800 and below will still require an exposure time too long to hand hold and still get sharp images. Most of mine were at 1/30s and longer.
- Yes, the X Pro 1 works well at high ISO settings, but in IR the camera will still create noise in the dark areas of the image.
-

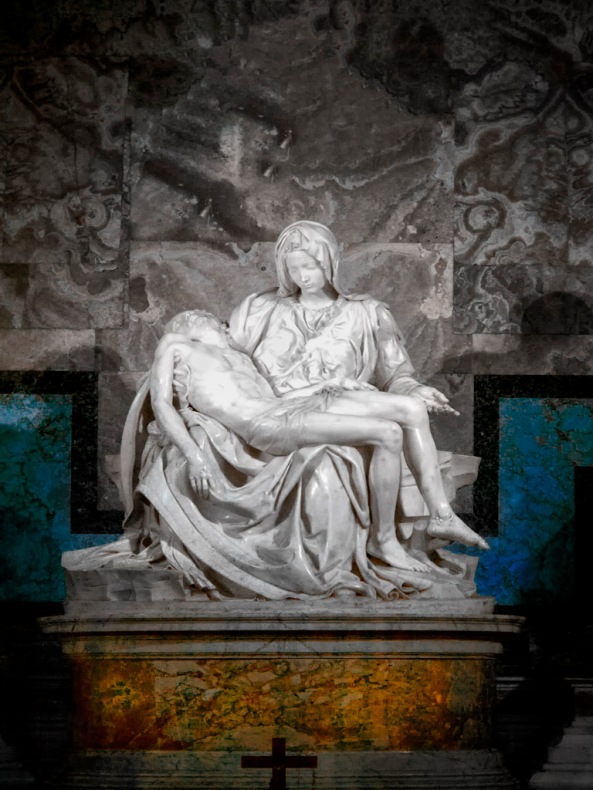
Fuji X Pro 1 with a custom WB right out of the camera. This is as close as you can get but will still generate a great image.
White Balance is IMPORTANT when shooting in IR! The X Pro 1 will NOT reliably do a custom white balance with the 720nm IR filter installed. But it does have a manual Kelvin White Balance option, so when shooting IR you need to go to this sub menu in the WB settings and set it to 2500K. I have talked to others doing this and have heard that they also take away green as well in the menu. I personally think that this is unnecessary and by leaving the green neutral you will get more pleasing Faux Color images. A properly white balanced image taken on your camera has s slight reddish cast, the sky should be bronze and the green leaves should have a monochromatic feel with a bluish cast. (more on this later) An improperly white balanced camera image will be pure dark red. While you can still use this image in post processing the lack of a good white balance will throw off your exposure system. Read your camera manual on white balance and understand it!
- Longer shutter speeds need a tripod to get sharp images!
- Remote shutter cable to cut down on camera shake!
- The Hoya R72 720nm IR filter will generate good Faux Color infrared images some of the time, but good B&W images all of the time. Keep this in mind while shooting and plan to always explore both options in post processing!
- Faux Color IR images require a channel swap in post processing. ONLY the Photoshop family (CS through CS6) has this function built in! Photoshop Elements has an optional plugin called Elements Plus that you can purchase to do this. Lightroom and Aperture DO NOT have this function!
Ok, enough of this for now. Lets talk images…
The Hoya R72 IR filter is almost black. You can see very little through it but don’t worry, the camera can see through it just fine! You can find these filters on Amazon for about $58.00 in 52mm. There are a lot of other filter companies out there that make these, some good some not so good… I trust the Hoya!
Mount the filter on your lens, set the ISO to around 1000 and put the camera on a tripod. Make sure that you have properly set the WB either as a custom on or as a Kelvin entry. If you choose custom, the camera will require a lot of light to due this properly. Use green grass to generate the custom white balance.
I like to use the optical viewfinder rather then the LCD or EVF for shooting in IR. Choose and frame your subject carefully. Hmm, a word about composition…
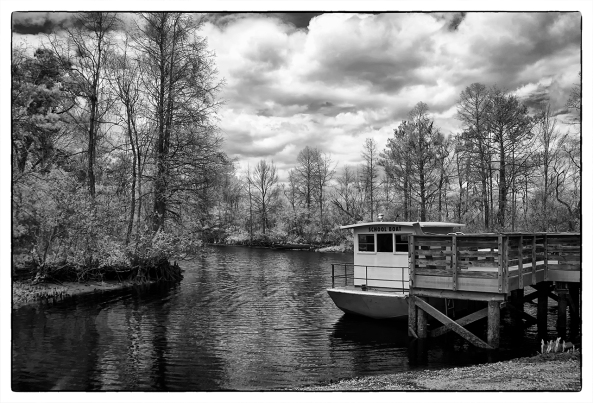
There are three items that can make IR images really powerful and full of emotional impact:
- Sky with clouds!
- Water reflections!
- Green Leaves!
The more of these items you can get in your images the better they will be! Here is an example…
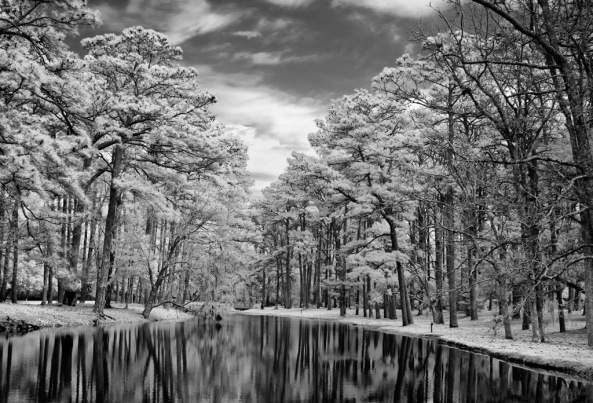

Clouds, Water and Leaves! What more could you ask for? While not done on a X Pro 1, this image could just have well been so!
As you can see, the sky, reflections and leaves create an emotionally packed, etherial image that draws your viewer into it! Keep these three compositional elements in mind as you go forth and create your images!
Exposure Issues…
OK, last part of this post! There are a few small exposure issues that you need to be aware of while doing IR work. They are:
- Red Channel over exposure: The RED channel will aways expose a stop or more higher than the blue and green. After you have taken the image and see the preview on the LCD panel look at the histogram. It only displays the combination monochrome histogram and if it is close to being overexposed you will get better results by dialing in -1ev exposure compensation and re-take the image. This is due to the red channel being more sensitive to infrared and causing the overexposure. You can really see this during the RAW conversion or in photoshop during post processing by looking at the RGB histogram there.
- Hot Spots: Some people have reported hot spots in the center of their images when using the 18mm lens. I have NOT personally seen any evidence of this with my system as of yet. Hot spots are areas in the center of each picture that is usually a stop brighter. They are caused by light bouncing back and forth between the sensor and the lens elements. These are lens specific and very little can be done while taking the picture to stop or reduce them. BUT, the aperture can have a drastic effect on them! If you see these then try adjusting the aperture and review the results, you just might be surprised! You MUST ALWAYS use a lens hood when shooting in IR. This will also help stop hot spots by stopping light from striking the objective lens at extreme angles then bouncing around inside the lens between elements. If you do notice the hot spot you can remove it in post processing very easily by using Nik Filters Viveza. You use the selection point by placing it in the center of the spot and then reduce the brightness!
OK, this is enough for today. The next post will be a detailed Post Processing tutorial that will take you through both Faux Color and B&W processing. I even have a photoshop action that you can download to semi automate the channel swap and cut down your post processing time!
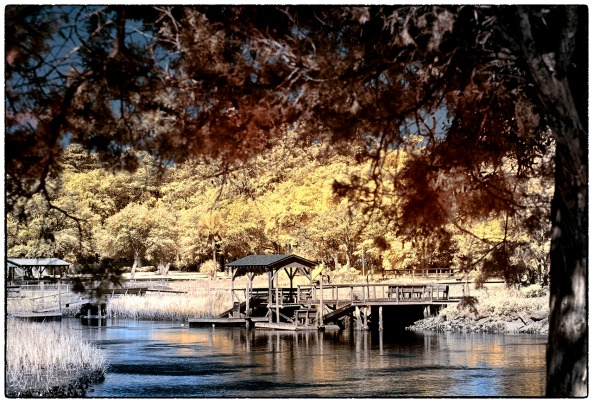
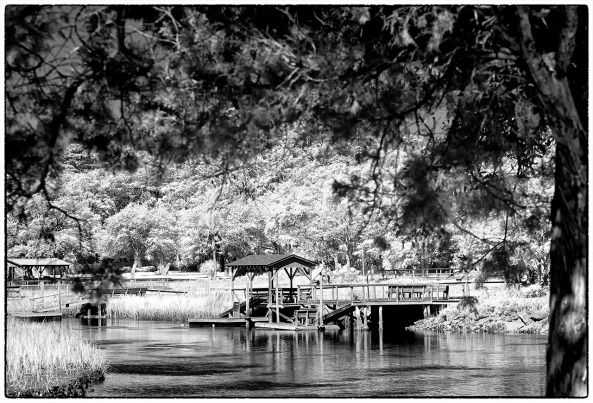



























 filter! This opens up an entire world for you to explore. The camera will see everything from UV to FULL COLOR to INFRARED! You simply tell it what you wish by your choice of external filter. If you only are interested in 590 nm, 620 nm and 665 nm then any digital camera will be fine for you. But if you wish to explore some of the alternatives, like the Super Blue (in camera Faux) or UV+IR (UG1) or the deep IR filters like 720nm (standard), 850nm (deep IR) and lower then you MUST have a camera with live view or full time LCD display! The reason for this is the fact that normal DSLR camera systems use an OPTICAL image path that goes from the viewfinder thru a prism, bounces off a mirror and out thru the lens and filter! If your filter is dark then you cannot see to compose although the camera will still focus! Live view will allow you to overcome this problem. There are some REALLY interesting filters out there like the UG1 (UV+IR) and the 047B (Super Blue in camera Faux) that will only work with an internal or Full Spectrum conversion but need a live view with the Full Spectrum Conversion! Now, the additional costs are the prices of the external filters to fit your lenses. The darker the filter the more they cost!
filter! This opens up an entire world for you to explore. The camera will see everything from UV to FULL COLOR to INFRARED! You simply tell it what you wish by your choice of external filter. If you only are interested in 590 nm, 620 nm and 665 nm then any digital camera will be fine for you. But if you wish to explore some of the alternatives, like the Super Blue (in camera Faux) or UV+IR (UG1) or the deep IR filters like 720nm (standard), 850nm (deep IR) and lower then you MUST have a camera with live view or full time LCD display! The reason for this is the fact that normal DSLR camera systems use an OPTICAL image path that goes from the viewfinder thru a prism, bounces off a mirror and out thru the lens and filter! If your filter is dark then you cannot see to compose although the camera will still focus! Live view will allow you to overcome this problem. There are some REALLY interesting filters out there like the UG1 (UV+IR) and the 047B (Super Blue in camera Faux) that will only work with an internal or Full Spectrum conversion but need a live view with the Full Spectrum Conversion! Now, the additional costs are the prices of the external filters to fit your lenses. The darker the filter the more they cost! 





















